v1.2.1
Tong Zhou
2025-11-02
v1.2.1.RmdOverview
This release (v1.2.1) extends dual-factor coloring support to
DATASET_COLORSTRIP and DATASET_STYLE,
continuing the enhancement of coloring functionality in the v1.2
series.
Updates:
-
Added:
DATASET_COLORSTRIPnow supports dual-factor coloring (main group + gradient). -
Added:
DATASET_STYLEnow supports dual-factor coloring (main group + gradient). -
Added: The third element of
colorparameter can specify a color palette set for base hues in bothDATASET_COLORSTRIPandDATASET_STYLE. -
Enhanced: New
darken_color()function with smart color enhancement for better visual appearance. -
Improved: Smart background color adjustment in
DATASET_STYLEdual-factor mode with enhanced contrast preservation.
1. DATASET_COLORSTRIP Dual-Factor Coloring
Following the same strategy as TREE_COLORS,
DATASET_COLORSTRIP now supports dual-factor coloring where
the first factor serves as the main grouping, and the second factor
creates gradients within each main group.
Minimal example
library(itol.toolkit)
library(dplyr)
# Load dataset4
tree_1 <- system.file("extdata","dataset4/otus.contree",package = "itol.toolkit")
data_file_1 <- system.file("extdata","dataset4/annotation.txt",package = "itol.toolkit")
data_1 <- data.table::fread(data_file_1)
# Create unit with dual-factor coloring (Class as main factor, Family as gradient)
u_colorstrip <- create_unit(
data = data_1 %>% select(ID, Class, Family),
key = "CS_dual",
type = "DATASET_COLORSTRIP",
color = c("Class", "Family", "nejm"),
tree = tree_1
)
write_unit(u_colorstrip)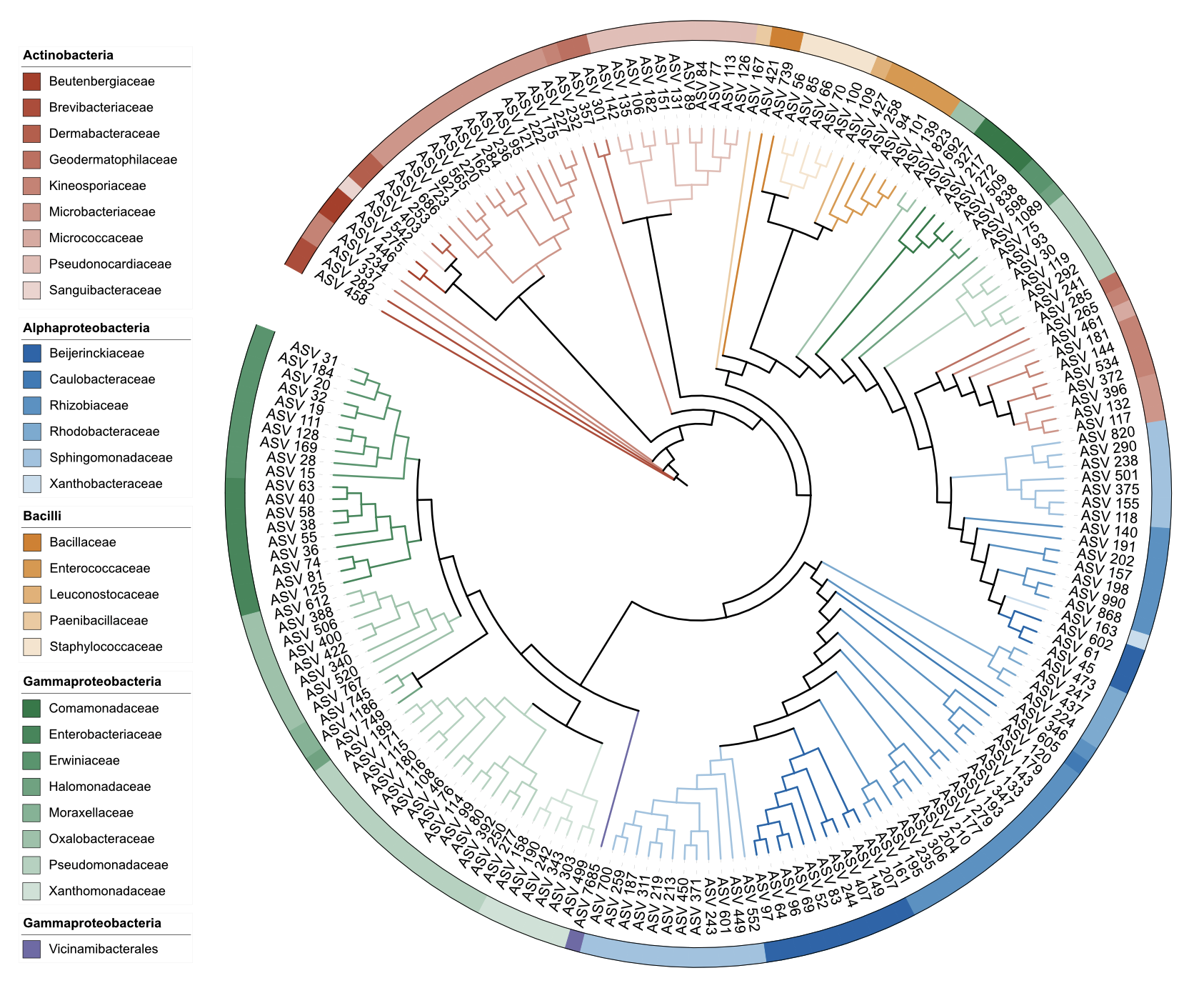
DATASET_COLORSTRIP dual-factor coloring example
With custom color palette
# Use wesanderson color palette for base colors
u_colorstrip_palette <- create_unit(
data = data_1 %>% select(ID, Class, Family),
key = "CS_dual_palette",
type = "DATASET_COLORSTRIP",
color = c("Class", "Family", "wesanderson"),
tree = tree_1
)
write_unit(u_colorstrip_palette)Single factor comparison
# Traditional single factor coloring for comparison
u_colorstrip_single <- create_unit(
data = data_1 %>% select(ID, Class),
key = "CS_single",
type = "DATASET_COLORSTRIP",
color = "wesanderson",
tree = tree_1
)
write_unit(u_colorstrip_single)2. Enhanced Color Darkening Function
v1.2.1 introduces a new darken_color() function that
intelligently enhances colors while preserving their natural appearance.
This is particularly useful for background colors that need to be
darkened but should maintain their original hue and saturation.
Function Overview
The darken_color() function provides three methods for
color darkening:
-
"proportional": Reduces RGB components proportionally (default method) -
"gradient": Uses gradient_color function with a dark target -
"enhanced": Smart method that preserves saturation for neutral colors
Enhanced Method Demonstration
library(itol.toolkit)
# Test colors with different saturation levels
test_colors <- c("#EAC4BE", "#F1D8D4", "#CCE2F0", "#BC3C29", "#0072B5")
# Compare different darkening methods
for(color in test_colors){
cat("Color:", color, "\n")
cat(" Proportional:", darken_color(color, factor = 0.4, method = "proportional"), "\n")
cat(" Enhanced:", darken_color(color, factor = 0.4, method = "enhanced"), "\n")
cat("\n")
}Smart Color Enhancement
The enhanced method is particularly effective for neutral colors (low saturation) that tend to become grayish when darkened using traditional methods:
- Neutral colors (saturation < 60): Uses a saturated dark target instead of pure black
- Saturated colors (saturation ≥ 60): Uses proportional darkening for efficiency
- Result: Maintains natural color appearance while providing adequate contrast
3. DATASET_STYLE Dual-Factor Coloring
DATASET_STYLE also supports dual-factor coloring with
the same strategy. This is particularly useful for styling tree branches
and labels with hierarchical color schemes.
Example 1: Branch styling in clade position
# Dual-factor coloring for branch styling in clade position
u_style_branch_clade <- create_unit(
data = data_1 %>% select(ID, Class, Family),
key = "STYLE_branch_clade_dual",
type = "DATASET_STYLE",
subtype = "branch",
color = c("Class", "Family", "nejm"),
position = "clade",
line_type = "normal",
size_factor = 5,
tree = tree_1
)
write_unit(u_style_branch_clade)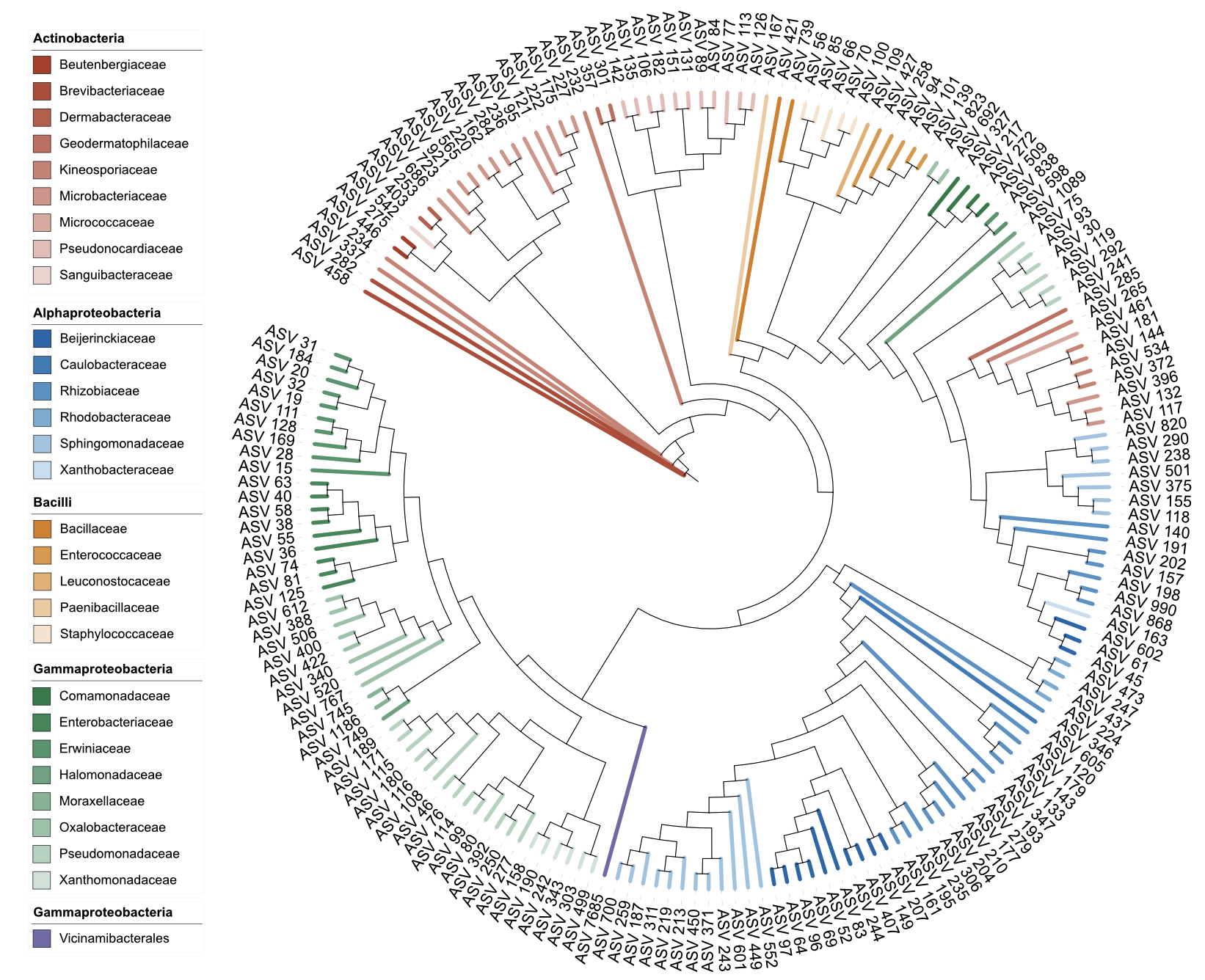
Branch styling in clade position (dual-factor coloring)
Example 2: Branch styling in node position
# Dual-factor coloring for branch styling in node position
u_style_branch_node <- create_unit(
data = data_1 %>% select(ID, Class, Family),
key = "STYLE_branch_node_dual",
type = "DATASET_STYLE",
subtype = "branch",
color = c("Class", "Family", "nejm"),
position = "node",
line_type = "dashed",
size_factor = 3,
tree = tree_1
)
write_unit(u_style_branch_node)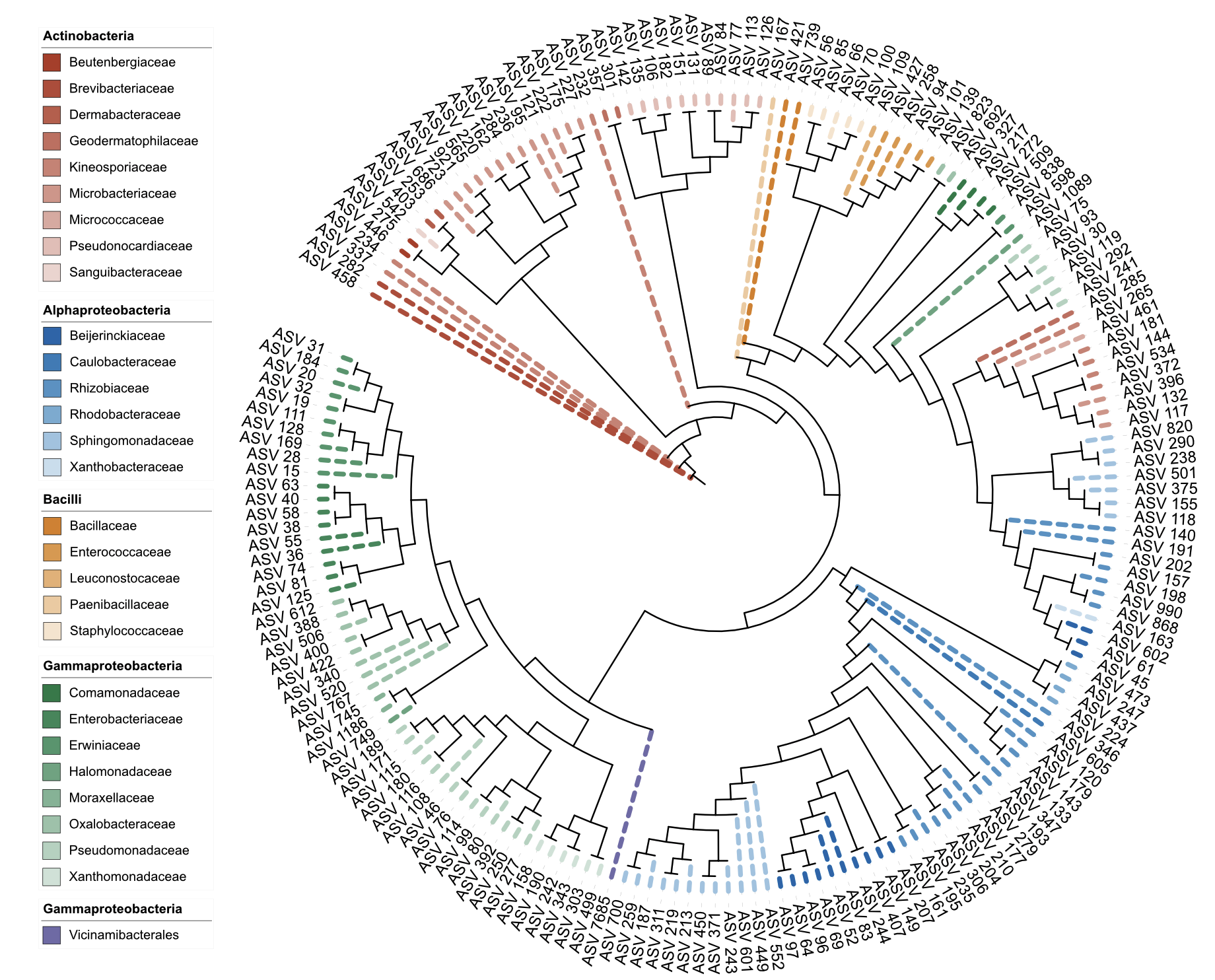
Branch styling in node position (dual-factor coloring)
Example 3: Label styling in node position
# Dual-factor coloring for label styling in node position
u_style_label_node <- create_unit(
data = data_1 %>% select(ID, Class, Family),
key = "STYLE_label_node_dual",
type = "DATASET_STYLE",
subtype = "label",
color = c("Class", "Family", "nejm"),
position = "node",
font_type = "bold",
size_factor = 1.5,
tree = tree_1
)
write_unit(u_style_label_node)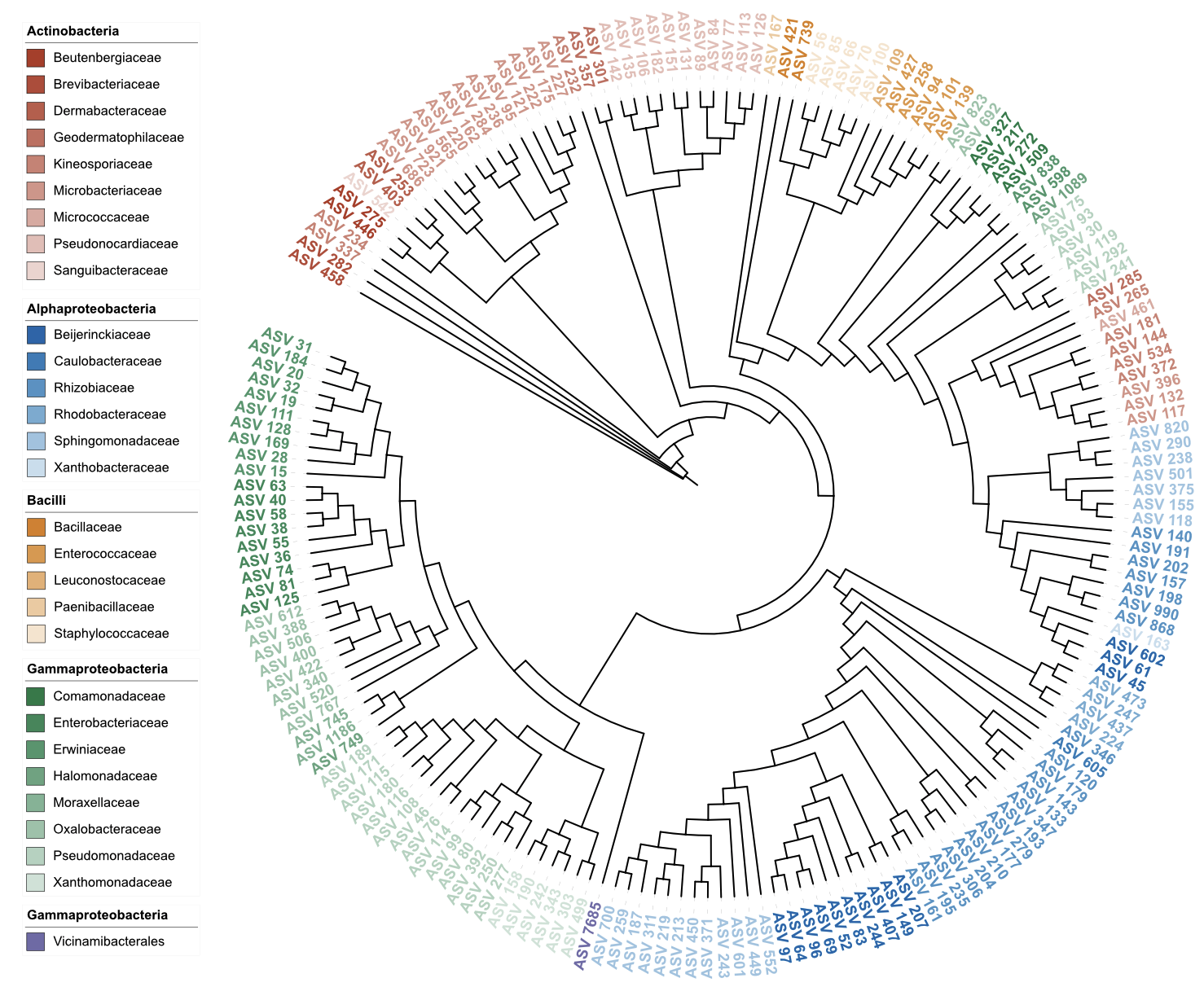
Label styling in node position (dual-factor coloring)
Example 4: Label styling in clade position
# Dual-factor coloring for label styling in clade position
u_style_label_clade <- create_unit(
data = data_1 %>% select(ID, Class, Family),
key = "STYLE_label_clade_dual",
type = "DATASET_STYLE",
subtype = "label",
color = c("Class", "Family", "nejm"),
position = "clade",
font_type = "italic",
size_factor = 1.5,
tree = tree_1
)
write_unit(u_style_label_clade)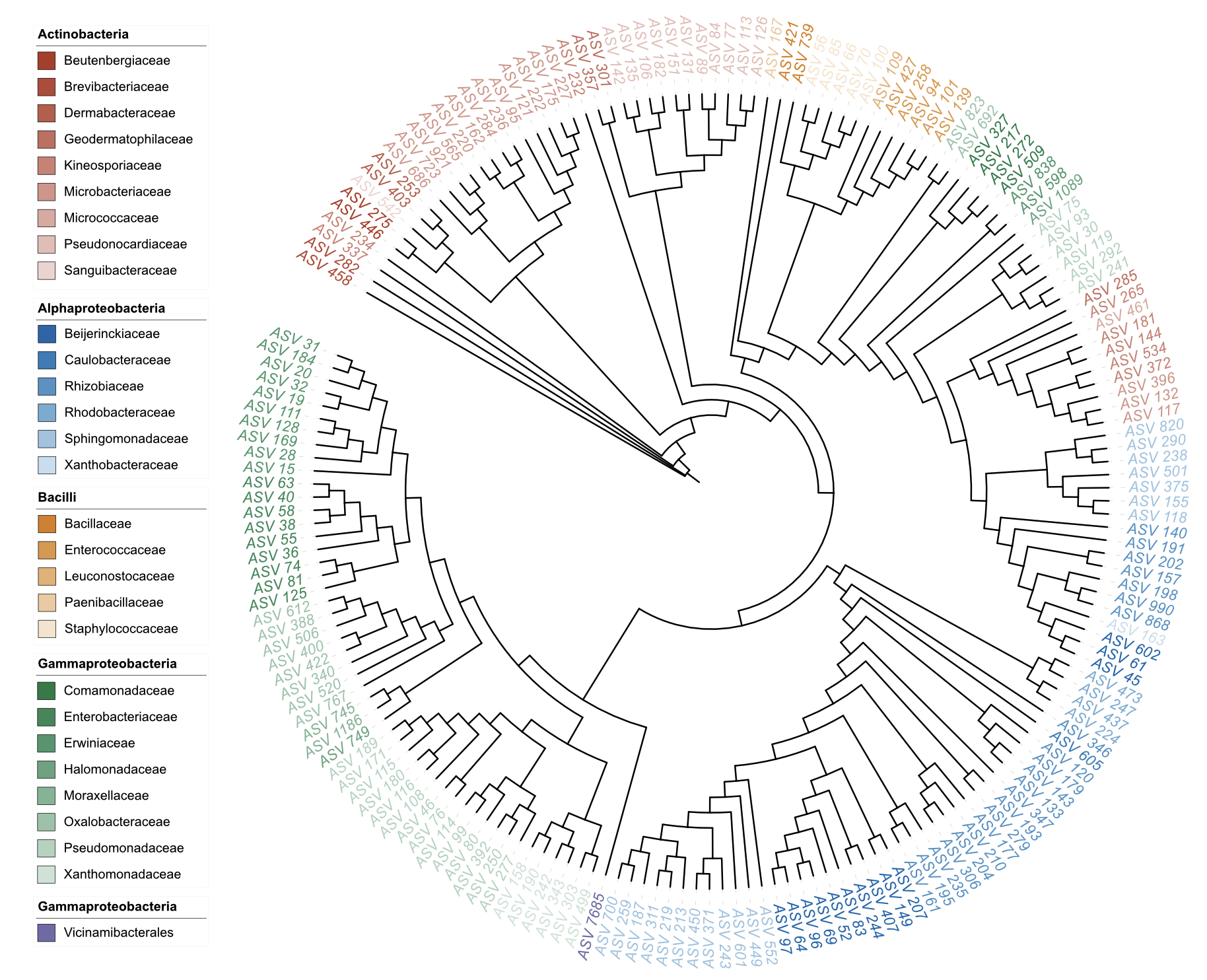
Label styling in clade position (dual-factor coloring)
Example 5: Label styling with dual-factor background color
# Dual-factor coloring for both label and background color
# When background_color matches color parameter, background uses dual-factor coloring with smart contrast adjustment
# - For colors with good contrast: 70% adjustment towards white
# - For light colors (distance to white < 80): enhanced darkening to preserve color hue and saturation
u_style_label_bg_dual <- create_unit(
data = data_1 %>% select(ID, Class, Family),
key = "STYLE_label_bg_dual",
type = "DATASET_STYLE",
subtype = "label",
color = c("Class", "Family", "nejm"),
background_color = c("Class", "Family", "nejm"), # Same as color parameter triggers dual-factor background
position = "clade",
font_type = "bold-italic",
size_factor = 1.5,
tree = tree_1
)
write_unit(u_style_label_bg_dual)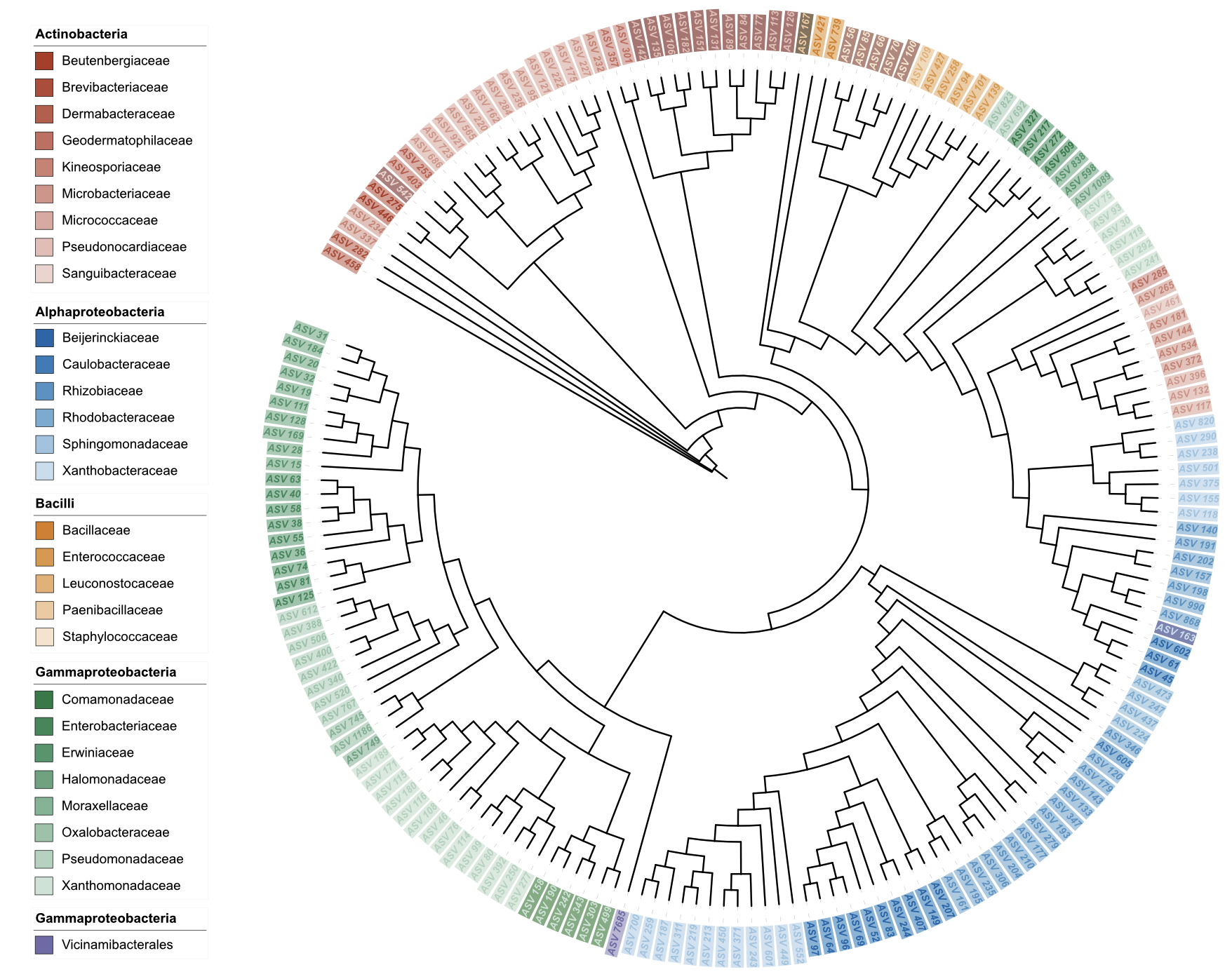
Label styling with dual-factor background color
Example 6: Label styling with dual-factor background only
# Dual-factor coloring for background only, keeping label color uniform
# This demonstrates background_color dual-factor without affecting the main color
u_style_bg_only <- create_unit(
data = data_1 %>% select(ID, Class, Family),
key = "STYLE_bg_only_dual",
type = "DATASET_STYLE",
subtype = "label",
color = "#000000", # Uniform black label color
background_color = c("Class", "Family", "nejm"), # Dual-factor background
position = "clade",
font_type = "bold",
size_factor = 1.5,
tree = tree_1
)
write_unit(u_style_bg_only)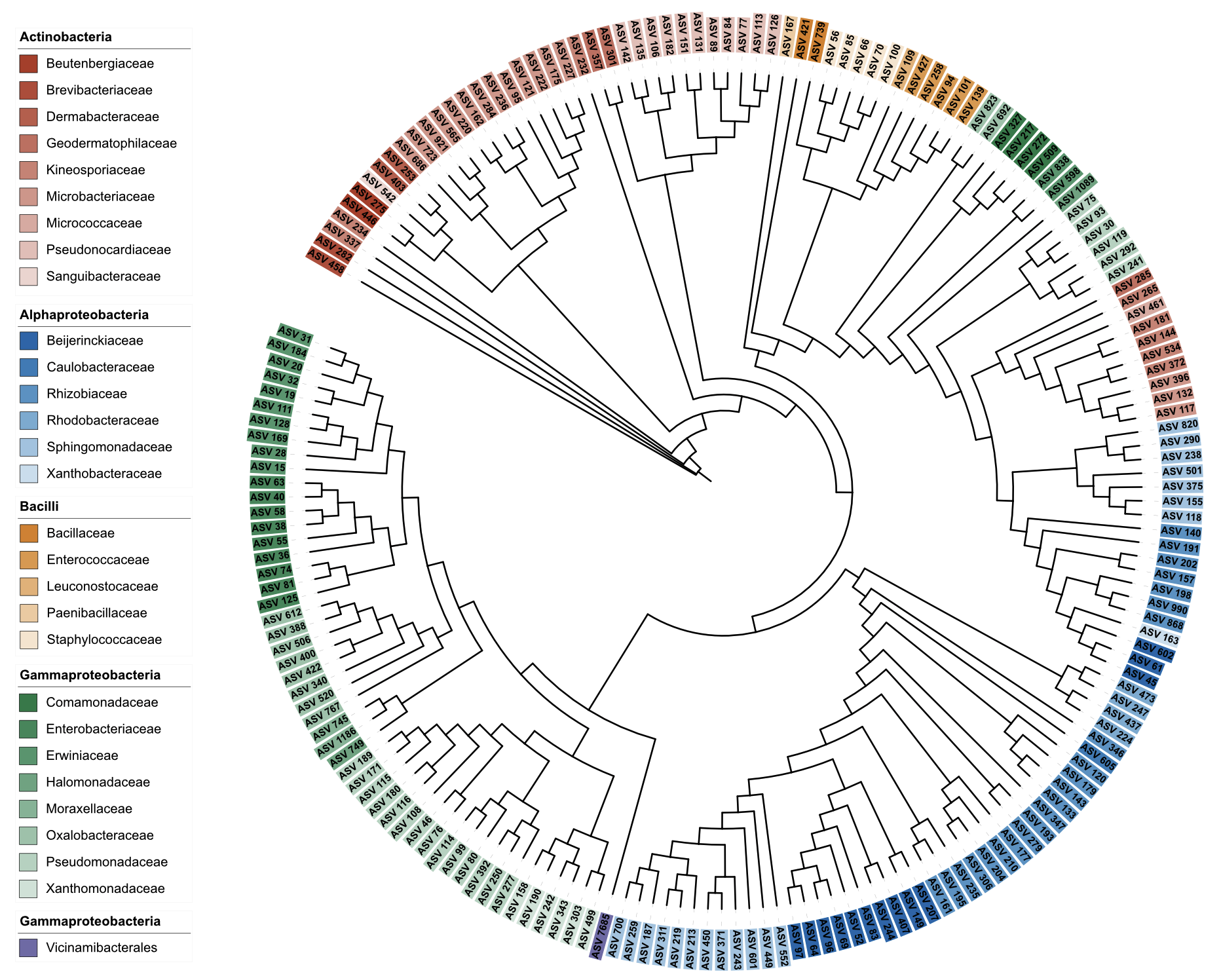
Label styling with dual-factor background only
Example 7: Label styling with uniform background color
# Traditional uniform background color for comparison
u_style_label_bg_uniform <- create_unit(
data = data_1 %>% select(ID, Class, Family),
key = "STYLE_label_bg_uniform",
type = "DATASET_STYLE",
subtype = "label",
color = c("Class", "Family", "nejm"),
background_color = "#000000", # Single color for uniform background
position = "clade",
font_type = "bold-italic",
size_factor = 1.5,
tree = tree_1
)
write_unit(u_style_label_bg_uniform)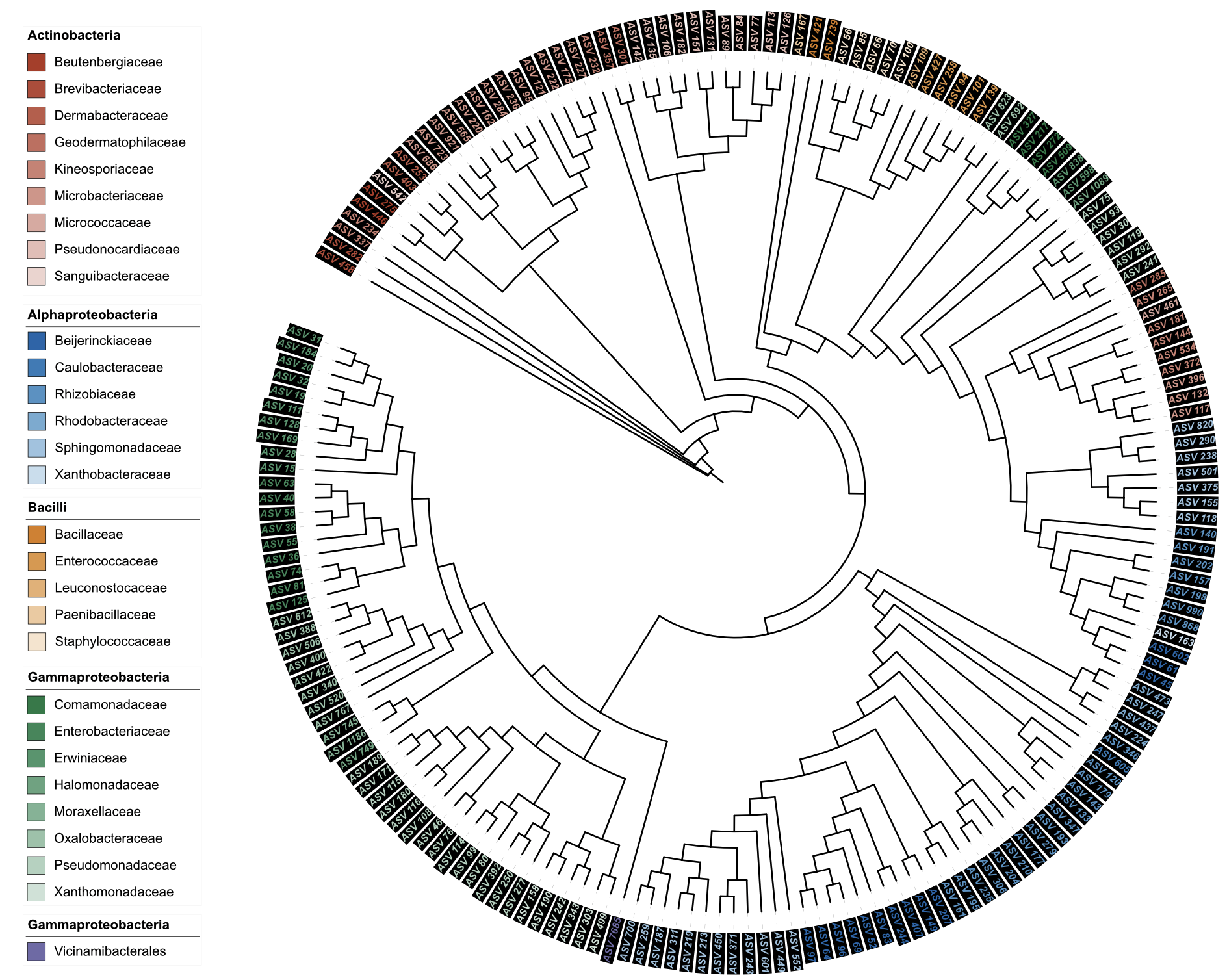
Label styling with uniform background color
Single factor comparison
# Traditional single factor coloring for comparison
u_style_single <- create_unit(
data = data_1 %>% select(ID, Class),
key = "STYLE_single",
type = "DATASET_STYLE",
subtype = "label",
color = "table2itol",
position = "node",
font_type = "normal",
size_factor = 1,
tree = tree_1
)
write_unit(u_style_single)4. Implementation Details
The dual-factor coloring implementation for both
DATASET_COLORSTRIP and DATASET_STYLE follows
the same logic as TREE_COLORS:
- Main factor: Determines the base color for each group
- Gradient factor: Creates color gradients within each main group
-
Background color: When
background_colorparameter matchescolorparameter exactly, enables dual-factor background coloring with smart contrast adjustment- Uses
color_distance()function to calculate color contrast - For colors with good contrast (distance ≥ 80): 70% adjustment towards white
- For light colors (distance < 80): smart darkening using
darken_color()function with “enhanced” method to preserve color hue and saturation
- Uses
-
Color enhancement: The new
darken_color()function provides intelligent color darkening- Enhanced method: For neutral colors (saturation < 60), uses saturated dark targets instead of pure black
- Proportional method: For saturated colors, uses traditional proportional RGB reduction
- Result: Maintains natural color appearance while providing adequate contrast
- Legend: Uses the gradient factor name as title, with labels ordered by main factor grouping, then alphabetically within groups
- DATA block: Uses the gradient factor values as labels
5. Usage Notes
- The
colorparameter accepts either:- Single value:
color = "Class"(traditional single factor) - Two values:
color = c("Class", "Family")(dual-factor with default palette) - Three values:
color = c("Class", "Family", "nejm")(dual-factor with custom palette)
- Single value:
- Available color palettes include:
table2itol,wesanderson,RColorBrewer, etc. - Legend title automatically uses the gradient factor name for clarity
- Both
DATASET_COLORSTRIPandDATASET_STYLEsupport the same dual-factor coloring syntax - For
DATASET_STYLE, whenbackground_colormatchescolorparameter exactly, background colors follow dual-factor scheme with smart contrast adjustment - Smart background color selection:
- For colors with good contrast: 70% adjustment towards white
- For light colors (distance to white < 80): smart darkening using
darken_color()function with “enhanced” method to preserve color hue and saturation
- Background color examples:
- Uniform:
background_color = "#000000"(single color) - Dual-factor:
background_color = c("Class", "Family", "nejm")(matches color parameter) - Background-only dual-factor:
background_color = c("Class", "Family", "nejm")withcolor = "#000000"
- Uniform:
- Color enhancement function:
-
darken_color(color, factor = 0.4, method = "enhanced")for neutral colors -
darken_color(color, factor = 0.4, method = "proportional")for saturated colors - Available methods: “proportional”, “gradient”, “enhanced”
-